Docker is a software platform that simplifies the process of building, running, managing and distributing applications using virtualization. It's different from traditional virtual machines because the virtualization is done at an operating system level.
Docker's architecture comprises three main components:
Docker Client: Interface through which the user interacts with docker. It communicates with the Docker daemon.
Docker Host: The Docker daemon listens for Docker API requests and manages various Docker objects.
Dockers Registry: This is where docker images are stored. Docker Hub, for instance, is a widely used public registry.
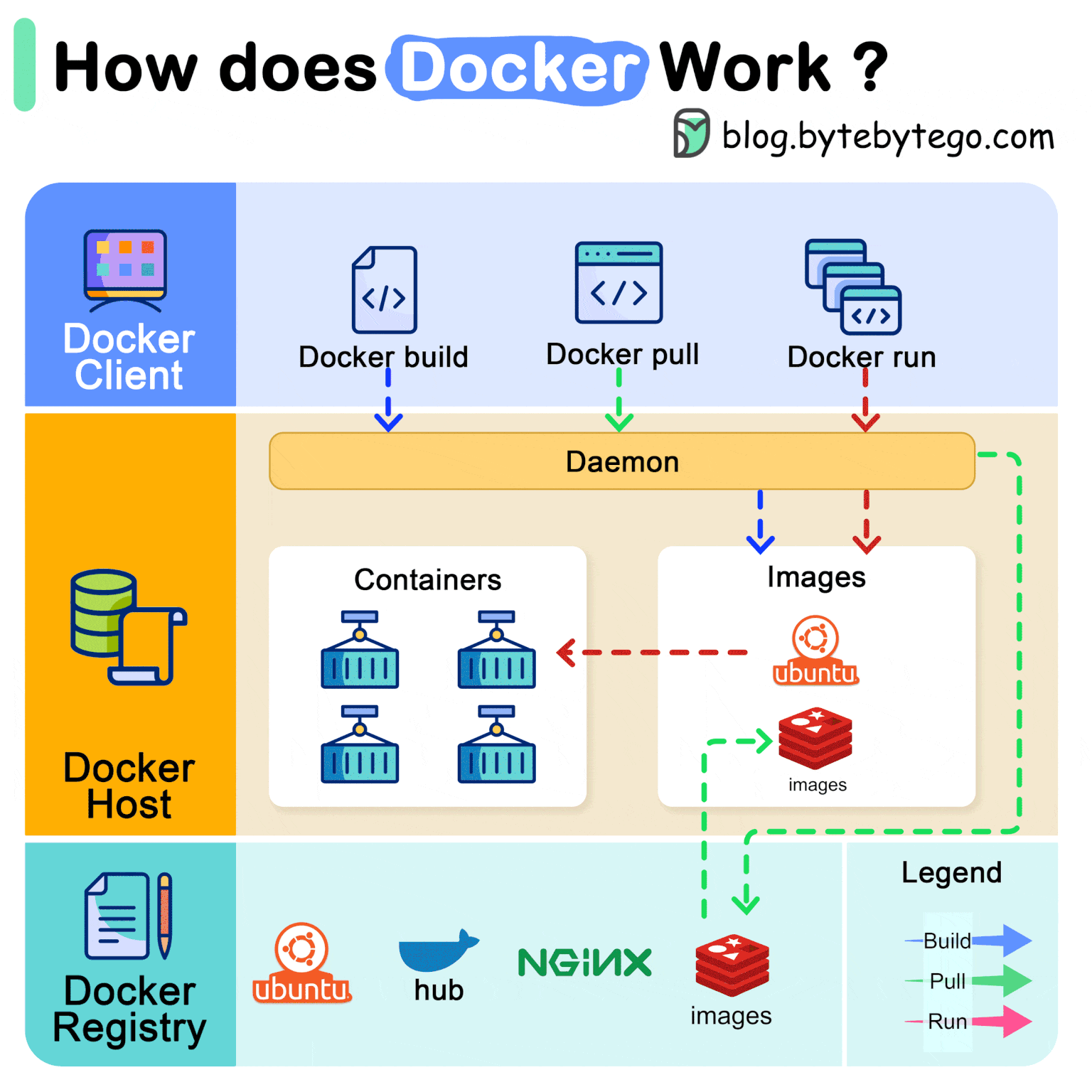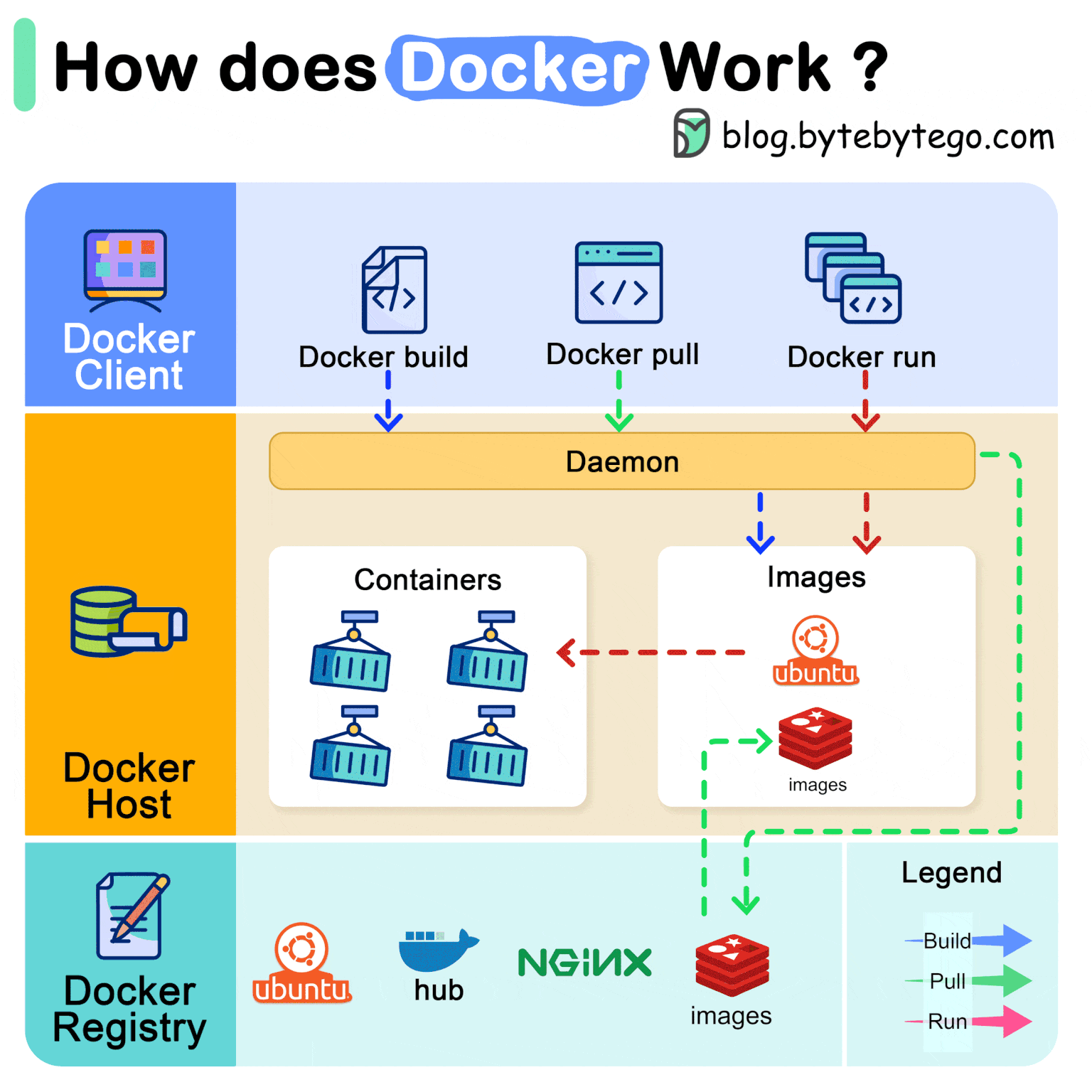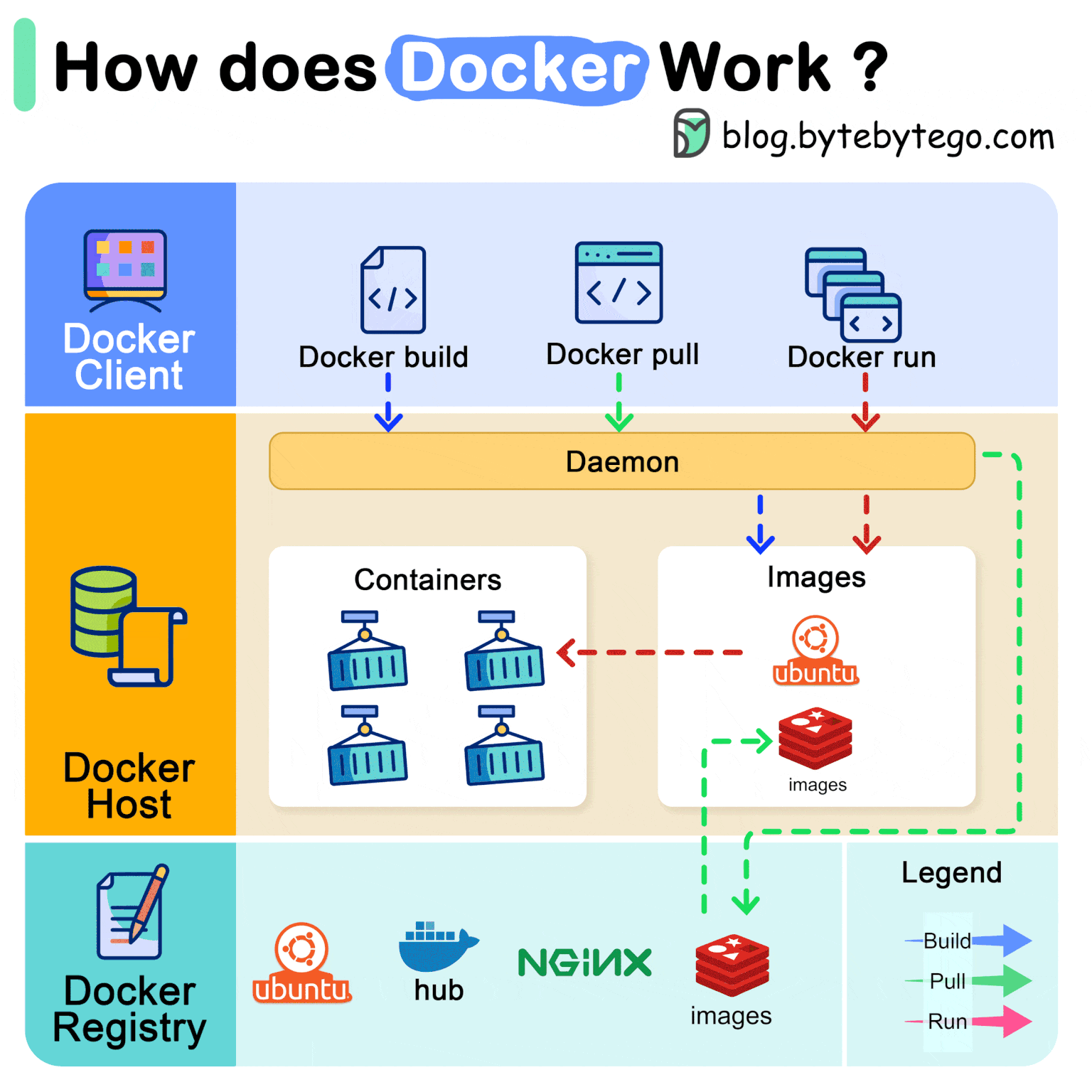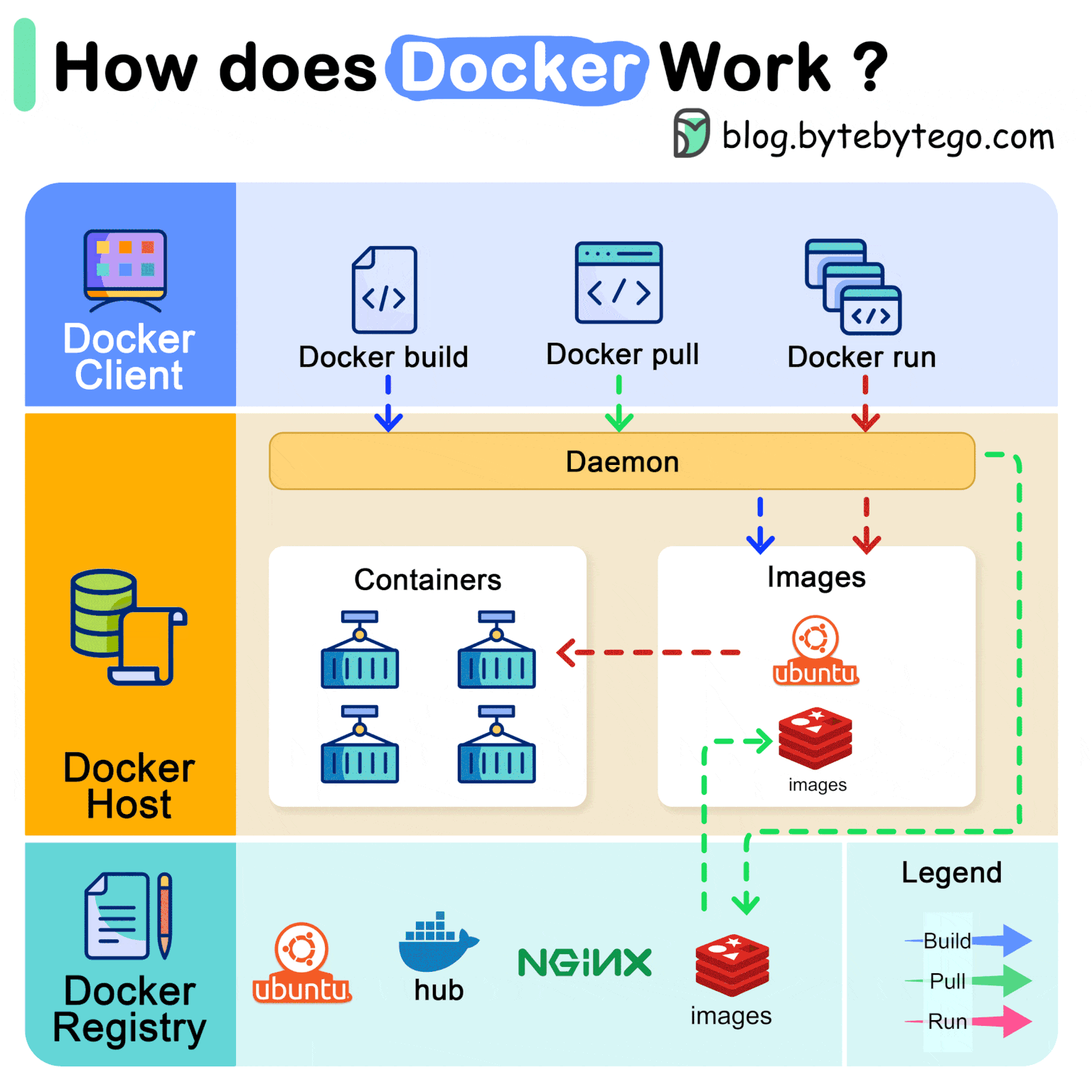
As an example, let's set up a WordPress instance using docker images.
docker run -d --name wp-database -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=12345 mysql:latest
Now let's look inside it
docker exec -it wp-database bash
The parameter -i state that we must keep STDIN open from the container and the -t assigns a pseudo-tty to the container providing us with an interactive shell.
We can invoke regular Linux commands here, in fact, if you check the disk usage
df -h
You will see the container seems to be using the native file system, well, that is what virtualization at the operating system level means.
Now we can log into the Mysql database and create a database to be used by the wp-website:
mysql -u root -p
create database wordpress
Now let's do the same we did for the database but now to create a container with a WordPress installation:
docker run -d --name wp-website -p 8888:80 wordpress
We now need to create a connection between wp-database and wp-website because otherwise they cannot see each other.
docker network create --attachable wp-network
docker network connect wp-network wp-database
docker network connect wp-network wp-website
For more detailed information about the docker network check this YouTube video: youtube.com/watch?v=bKFMS5C4CG0
Accessing localhost:8888 we can see WordPress's initial wizard
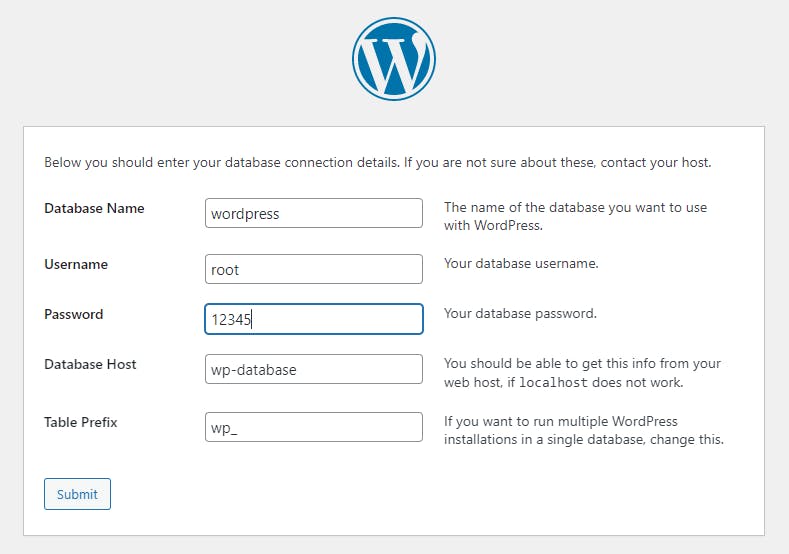
You can now manage those containers with
docker ps
docker ps -a
docker stats
docker stop wp-website wp-database
docker start wp-website wp-database
If you want an easier way to manage your containers, you can always install a container to manage your containers through a web interface.
docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --name portainer --restart always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer
It's like having a coffee table book about coffee tables
